Fitting Regression Trees
Following the previous implementation of Decision Trees Classifier, this note covers the implementation of Decision Trees Regression.
# loading the necessary libraries
# keep in mind that some libraries need installing
library(ISLR)
library(ggthemr)
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyverse)
library(tidymodels)
library(rpart.plot)# loading the ames dataset
data("ames")
head(ames, n=10)The response variable from the dataset is the Sale_Price. As see on the data overview, there are a number of variables/features that are part of the dataset. We will fit all of these features into the Tree Model.
# for reproducibility
set.seed(5672)
ames_split <- initial_split(ames, prop = .8)
# training datasets
train_data <- training(ames_split)
test_data <- testing(ames_split)
dim(train_data); dim(test_data);# fitting a regression
decision_tree_regression <- decision_tree() %>%
set_engine("rpart") %>%
set_mode("regression")# fitting a regression tree
reg_tree_fit <- fit(decision_tree_regression, data = train_data, formula = Sale_Price ~ .)
reg_tree_fitPruning Complexity Parameter
The rpart engine performs a range of cost complexity assessments even with the base model. It performs a 10-fold CV by default. The plotcp() method provides us with the visualization of the validation and a way to choose the number of terminal nodes to use. In the visualization below, 11 nodes seem to be best performing.
reg_tree_fit %>%
extract_fit_engine() %>%
plotcp()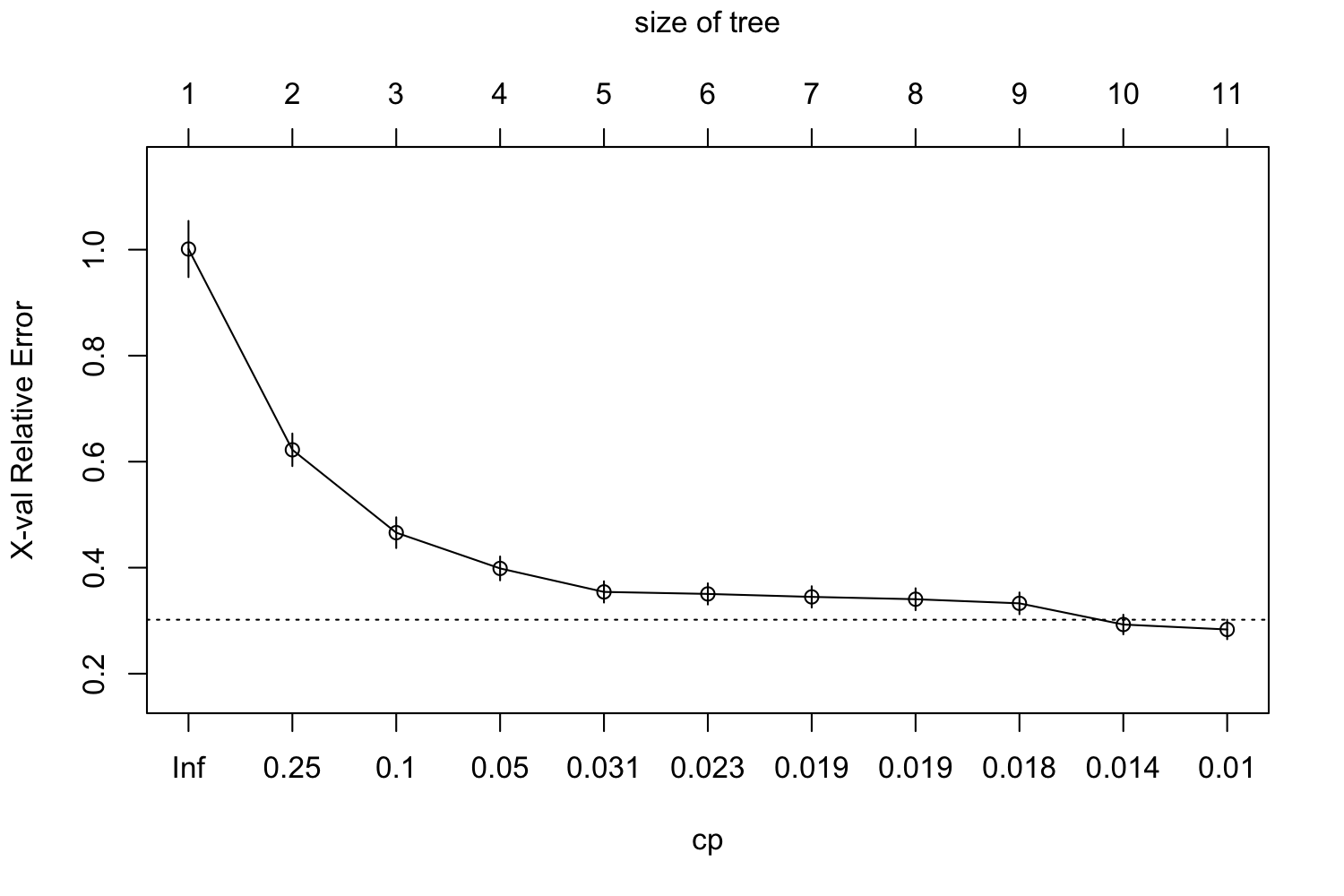
Model Fit Assessment and Tree Visualization
As this is a regression task, we can extract regression model assessment metrics such as rmse to the dataset.
# showing the top predicted values
augment( reg_tree_fit, new_data = train_data ) %>%
rmse( truth = Sale_Price, estimate = .pred )reg_tree_fit %>%
extract_fit_engine() %>%
rpart.plot(roundint = FALSE) 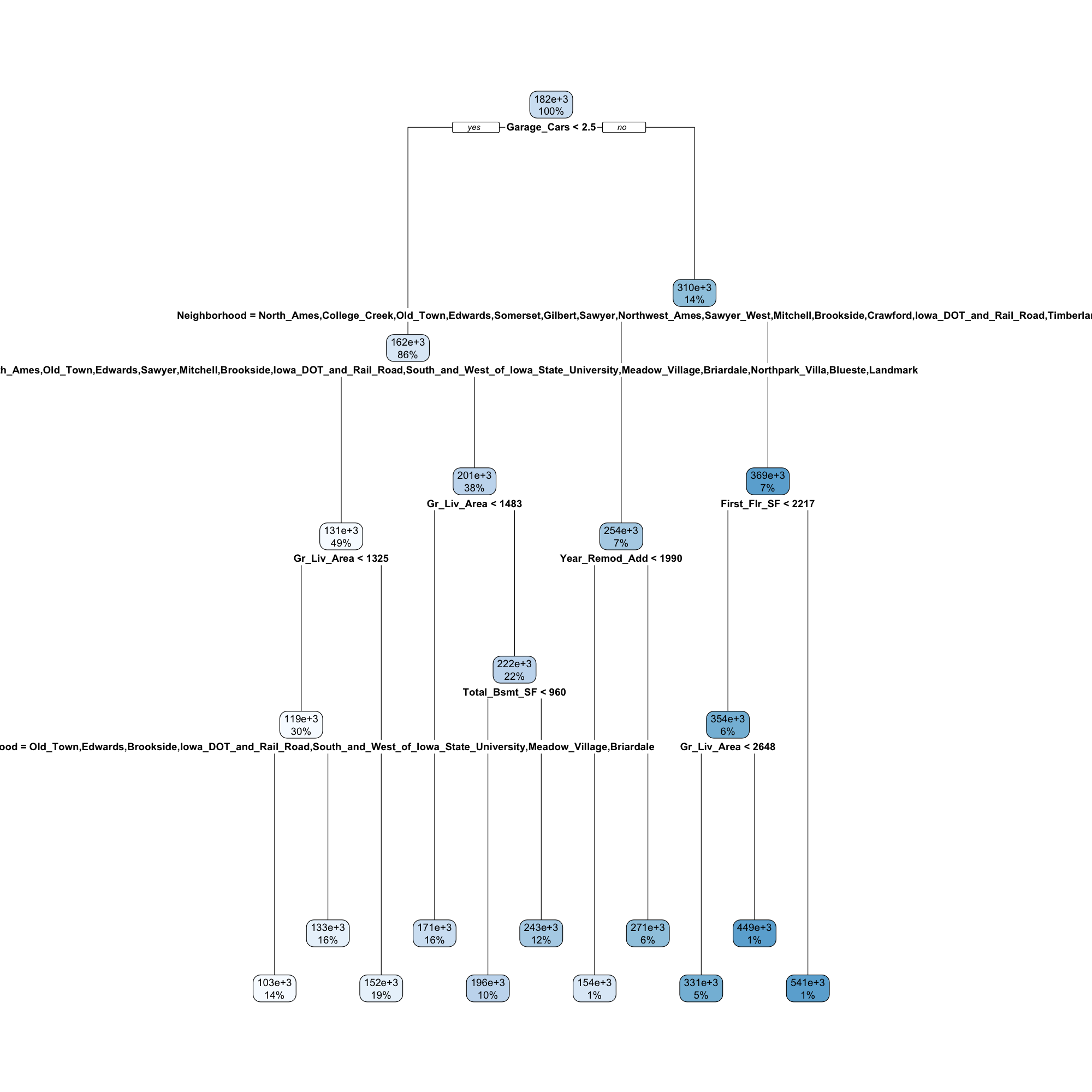
Predictions on Test and New Observations
We can then run predictions on the test data set and/or new observation in the same way we have with the train set above.
augment( reg_tree_fit, new_data = train_data ) %>%
rmse( truth = Sale_Price, estimate = .pred )