Translating Images
Translating images is the process of moving pixels in the $x$ and $y$ dimension by some specified magnitude. To achieve this, we define a matrix of the form:
$$\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & x \\ 0 & 1 & y \end{pmatrix} $$
where $x$ and $y$ are the respective number of pixels in the width and height dimension to translate/move the image
In the following example, we read an image and translate it to 500 pixels in $x$ and 700 pixels in $y$ direction.
Defining the translation matrix
import numpy as np
translation_matrix = np.float32([ [1, 0, 500], [0, 1, 700]])
translation_matrixarray([[ 1., 0., 500.],
[ 0., 1., 700.]], dtype=float32)
Reading an image for translation
import cv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
snow_mountain = cv2.imread('snow_mountain.jpg')
snow_mountain = cv2.cvtColor(snow_mountain, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 7))
plt.imshow(snow_mountain)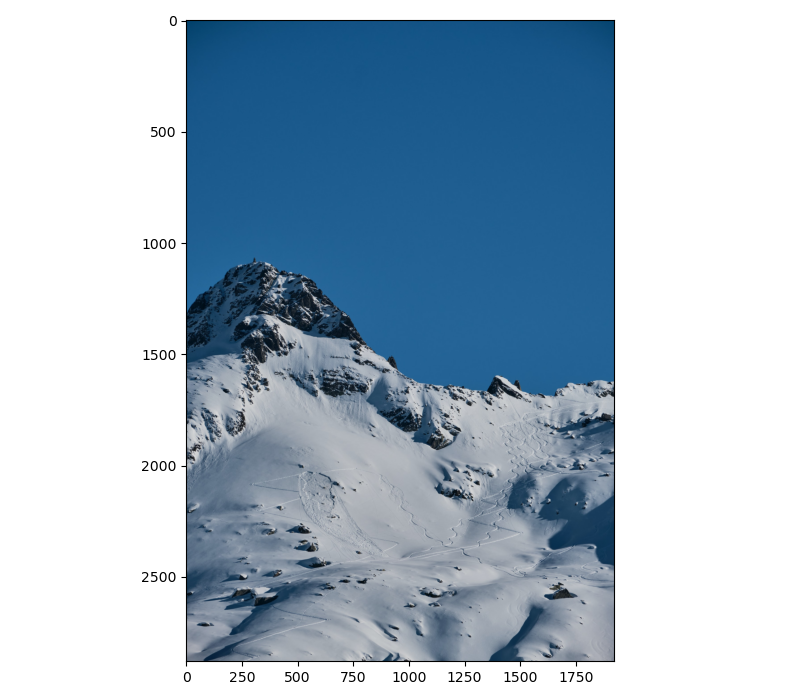
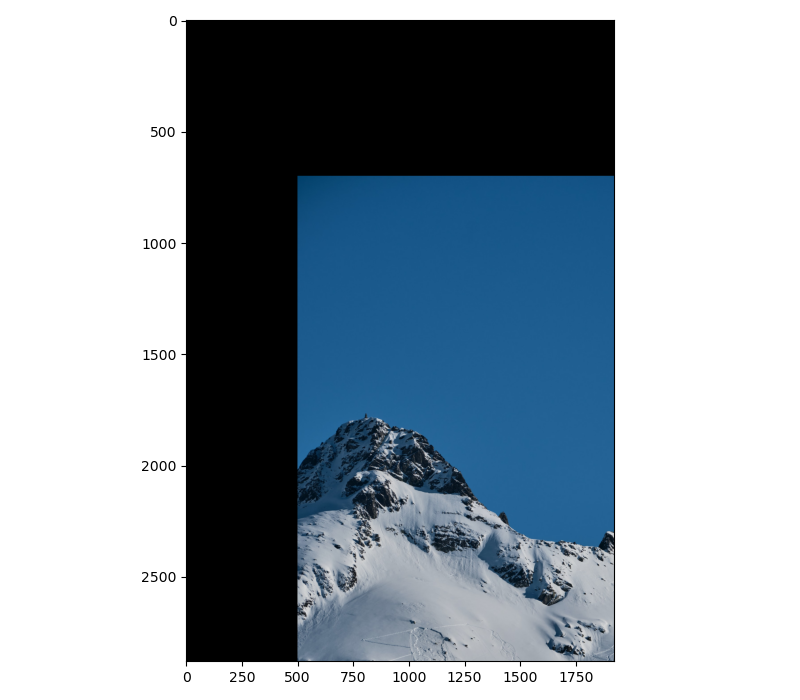
To implement the translation, call the $cv2.warpAffine() method, passing the image, translation matrix, and $x$ and $y$ output dimensions
translated_snow_mountain = cv2.warpAffine(snow_mountain, translation_matrix, (snow_mountain.shape[1], snow_mountain.shape[0]))plt.figure(figsize=(8, 7))
plt.imshow(translated_snow_mountain )